|
|||||
 |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
Discrete
|
|
Continuous
|
|
|
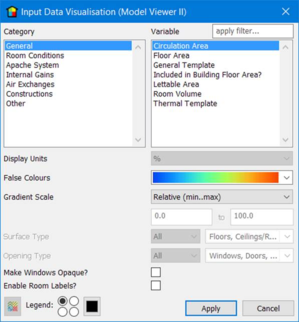
General Template
|
The general template assigned to the room.
|
|
|
Thermal Template
|
The thermal template assigned to the room.
|
|
|
Room Volume
|
The calculated volume of the room.
|
|
|
Floor Area
|
The calculated floor area of the room.
|
|
|
Lettable Area
|
The percentage of the floor area that is lettable.
|
|
|
Circulation Area
|
The percentage of the floor area that is classed as circulation.
|
|
|
Included in Building Floor Area?
|
Whether or not this zone contributes to the building floor area.
|
|
|
Heating Profile
|
A modulating profile scheduling the operation of the heating plant.
|
|
|
Heating Setpoint
|
The temperature set point for heating control. It can be constant or it can follow an absolute profile.
|
|
|
Cooling Profile
|
A modulating profile scheduling the operation of the cooling plant.
|
|
|
Cooling Setpoint
|
The temperature set point for cooling control. It can be constant or it can follow an absolute profile.
|
|
|
DHW Profile
|
Specifies the procedure for determining how the room’s DHW demand varies with time.
|
|
|
DHW Consumption*
|
The maximum rate of hot water consumption.
|
|
|
Aux Energy Profile
|
The modulating profile specifying the times when auxiliary energy will be incurred.
|
|
|
Solar Reflected Fraction
|
The fraction of solar radiation entering the room which is assumed to be scattered back out through glazing.
|
|
|
Furniture Mass Factor
|
An allowance for the thermal inertia of furniture.
|
|
|
Humidity Control Min
|
The minimum percentage saturation level to be maintained in the room during periods of plant operation, as specified by the Cooling profile.
|
|
|
Humidity Control Max
|
The maximum percentage saturation level to be maintained in the room during periods of plant operation, as specified by the Cooling profile.
|
|
|
Max Humidification
|
The maximum level of humidification calculated during a Loads run.
|
|
|
Max Dehumidification
|
The maximum level of dehumidification calculated during a Loads run.
|
|
|
Max Heating + Humidification
|
The maximum level of room unit heating plus humidification calculated during a Loads run.
|
|
|
Max Cooling + Dehumidification
|
The maximum level of room unit cooling plus dehumidification calculated during a Loads run.
|
|
|
HVAC System
|
The Apache System serving the room.
|
|
|
Aux Vent System
|
The Apache System handling auxiliary ventilation air exchanges.
|
|
|
DHW System
|
The Apache System that handles Domestic Hot Water.
|
|
|
Heating Unit Size
|
The maximum heating unit demand encountered during loads analysis.
|
|
|
Heating Unit Unlimited Capacity?
|
Whether or not there is unlimited capacity available from the heating units in the room.
|
|
|
Heating Unit Fixed Capacity
|
The maximum capacity available from the heating units in the room.
|
|
|
Heating Plant Radiant Fraction
|
The fraction of the heating plant’s output that is in the form of radiant, rather than convected, heat.
|
|
|
Cooling Unit Size
|
The maximum cooling unit demand encountered during loads analysis.
|
|
|
Cooling Unit Unlimited Capacity?
|
Whether or not there is unlimited capacity available from the cooling units in the room.
|
|
|
Cooling Unit Fixed Capacity
|
The maximum capacity available from the cooling units in the room.
|
|
|
Cooling Plant Radiant Fraction
|
The fraction of the cooling plant’s output that is in the form of radiant, rather than convected, heat.
|
|
|
System Air Supply Flow Rate
|
The maximum flow rate of air supplied to the room.
|
|
|
System Air Supply Free Cooling Flow Capacity
|
The maximum flow rate of external air available for providing free cooling to the room.
|
|
|
System Air Supply Variation Profile
|
A modulating profile specifying the time variation of the system supply air flow.
|
|
|
Has Mechanical Supply?
|
Whether or not the room is served by a mechanical ventilation air supply.
|
|
|
Mechanical Supply Specific Fan Power
|
The specific fan power to be used for the calculation of auxiliary energy associated with room-level ventilation supply.
|
|
|
Has Mechanical Exhaust?
|
Whether or not the room has mechanical ventilation extract.
|
|
|
Extract Flow Rate
|
The exhaust extract flow rate.
|
|
|
Mechanical Exhaust Specific Fan Power
|
The specific fan power to be used for the calculation of auxiliary energy associated with room-level ventilation extract.
|
|
|
Is Remote Extract Fan?
|
Whether or not the extract fan is outside of the room.
|
|
|
Lighting Max Sensible Gain
|
The peak sensible heat gain of the lighting gain.
|
|
|
Lighting Max Power Consumption
|
The peak rate of energy consumption of the lighting gain.
|
|
|
Lighting Max Illuminance
|
The illuminance value used to calculate the maximum sensible lighting gain.
|
|
|
Lighting Installed Power Density
|
The value used to calculate the maximum sensible lighting gain.
|
|
|
Lighting Radiant Fraction
|
The fraction of the lighting gain’s output that is in the form of radiant, rather than convected, heat.
|
|
|
Lighting Fuel
|
The type of fuel that the lighting gain uses.
|
|
|
Lighting Variation Profile
|
The modulating profile specifying the variation of the lighting gain throughout the year.
|
|
|
Lighting Dimming Profile
|
The modulating profile specifying the dimming variation of the lighting gain throughout the year.
|
|
|
Lighting Diversity Factor
|
The multiplicative factor applied in simulation runs for the lighting gain.
|
|
|
Lighting Ballast/Driver Fraction
|
The fraction of the Maximum Power Consumption that will be attributed to the ballast or LED driver of the lighting gain.
|
|
|
People Max Sensible Gain
|
The peak sensible heat gain of the people gain.
|
|
|
People Max Latent Gain
|
The peak latent heat gain of the people gain.
|
|
|
People Occupancy
|
The occupancy density for the specified people gain.
|
|
|
People Variation Profile
|
The modulating profile specifying the variation of the people gain throughout the year.
|
|
|
People Diversity Factor
|
The multiplicative factor applied in simulation runs for the people gain.
|
|
|
Computers Max Sensible Gain
|
The peak sensible heat gain of the computer gain.
|
|
|
Computers Max Power Consumption
|
The peak rate of energy consumption of the computer gain.
|
|
|
Computers Radiant Fraction
|
The fraction of the computer gain’s output that is in the form of radiant, rather than convected, heat.
|
|
|
Computers Fuel
|
The type of fuel that the computer gain uses.
|
|
|
Computers Variation Profile
|
The modulating profile specifying the variation of the computer gain throughout the year.
|
|
|
Computers Diversity Factor
|
The multiplicative factor applied in simulation runs for the computer gain.
|
|
|
Machinery Max Sensible Gain
|
The peak sensible heat gain of the machinery gain.
|
|
|
Machinery Max Latent Gain
|
The peak latent heat gain of the machinery gain.
|
|
|
Machinery Max Power Consumption
|
The peak rate of energy consumption of the machinery gain.
|
|
|
Machinery Radiant Fraction
|
The fraction of the machinery gain’s output that is in the form of radiant, rather than convected, heat.
|
|
|
Machinery Fuel
|
The type of fuel that the machinery gain uses.
|
|
|
Machinery Variation Profile
|
The modulating profile specifying the variation of the machinery gain throughout the year.
|
|
|
Machinery Diversity Factor
|
The multiplicative factor applied in simulation runs for the machinery gain.
|
|
|
Cooking Max Sensible Gain
|
The peak sensible heat gain of the cooking gain.
|
|
|
Cooking Max Latent Gain
|
The peak latent heat gain of the cooking gain.
|
|
|
Cooking Max Power Consumption
|
The peak rate of energy consumption of the cooking gain.
|
|
|
Cooking Radiant Fraction
|
The fraction of the cooking gain’s output that is in the form of radiant, rather than convected, heat.
|
|
|
Cooking Fuel
|
The type of fuel that the cooking gain uses.
|
|
|
Cooking Variation Profile
|
The modulating profile specifying the variation of the cooking gain throughout the year.
|
|
|
Cooking Diversity Factor
|
The multiplicative factor applied in simulation runs for the cooking gain.
|
|
|
Miscellaneous Max Sensible Gain
|
The peak sensible heat gain of the miscellaneous gain.
|
|
|
Miscellaneous Max Latent Gain
|
The peak latent heat gain of the miscellaneous gain.
|
|
|
Miscellaneous Max Power Consumption
|
The peak rate of energy consumption of the miscellaneous gain.
|
|
|
Miscellaneous Radiant Fraction
|
The fraction of the miscellaneous gain’s output that is in the form of radiant, rather than convected, heat.
|
|
|
Miscellaneous Fuel
|
The type of fuel that the miscellaneous gain uses.
|
|
|
Miscellaneous Variation Profile
|
The modulating profile specifying the variation of the miscellaneous gain throughout the year.
|
|
|
Miscellaneous Diversity Factor
|
The multiplicative factor applied in simulation runs for the miscellaneous gain.
|
|
|
Infiltration Max Flow
|
The total peak air change rate for all Infiltration air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Infiltration Variation Profile
|
The modulating profile(s) specifying the variation of the air flow throughout the year for all Infiltration air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Infiltration Adjacent Condition
|
The source(s) of air entering the room for all Infiltration air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Infiltration Adjacent Room
|
The adjacent room(s) from which the air is drawn for all Infiltration air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Infiltration Temperature Profile
|
The absolute profile(s) specifying the supply temperature for all Infiltration air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Infiltration Temperature Offset
|
The offset to be added to the external air temperature for all Infiltration air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Natural Max Flow
|
The total peak air change rate for all Natural air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Natural Variation Profile
|
The modulating profile(s) specifying the variation of the air flow throughout the year for all Natural air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Natural Adjacent Condition
|
The source(s) of air entering the room for all Natural air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Natural Adjacent Room
|
The adjacent room(s) from which the air is drawn for all Natural air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Natural Temperature Profile
|
The absolute profile(s) specifying the supply temperature for all Natural air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Natural Temperature Offset
|
The offset to be added to the external air temperature for all Natural air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Auxiliary Max Flow
|
The total peak air change rate for all Auxiliary air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Auxiliary Variation Profile
|
The modulating profile(s) specifying the variation of the air flow throughout the year for all Auxiliary air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Auxiliary Adjacent Condition
|
The source(s) of air entering the room for all Auxiliary air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Auxiliary Adjacent Room
|
The adjacent room(s) from which the air is drawn for all Auxiliary air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Auxiliary Temperature Profile
|
The absolute profile(s) specifying the supply temperature for all Auxiliary air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
Auxiliary Temperature Offset
|
The offset to be added to the external air temperature for all Auxiliary air exchanges in the room.
|
|
|
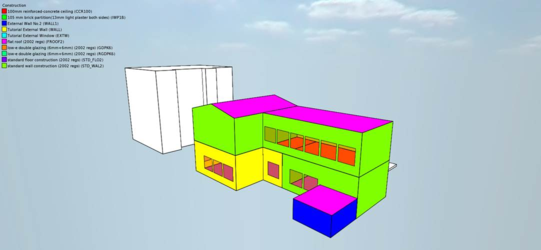
Construction
|
The construction name and id of all constructions in use.
|
|
|
Construction U-value
|
The U-value as calculated by the user selected method of all constructions in use.
Calculation methods: EN-ISO / CIBSE / ASHRAE.
|
|
|
Construction Net R-value
|
The total thermal resistance as calculated by the user selected method of all constructions in use.
Calculation methods: EN-ISO / CIBSE / ASHRAE.
|
|
|
Construction Total R-value
|
The total resistance of all layers of all constructions in use (does not include inside and outside surface resistances).
|
|
|
Construction Outside Surface Emissivity
|
The emissivity of the outside surface of all constructions in use.
|
|
|
Construction Inside Surface Emissivity
|
The emissivity of the inside surface of all constructions in use.
|
|
|
Construction Outside Surface Resistance
|
The thermal resistance between the outside of a surface and its environment for all constructions in use.
|
|
|
Construction Inside Surface Resistance
|
The thermal resistance between the inside of a surface and its environment for all constructions in use.
|
|
|
Construction Regs Thermal Bridging Coefficient
|
The heat loss as a multiple of element area for non-repeating thermal bridging used for UK Building Regulations compliance.
|
|
|
Construction Regs Data Source
|
The (generic or regulatory) data source of all constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Construction
|
The construction name and id of all opaque constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque U-value
|
The U-value as calculated by the user selected method of all opaque constructions in use.
Calculation methods: EN-ISO / CIBSE / ASHRAE.
|
|
|
Opaque Net R-value
|
The total thermal resistance as calculated by the user selected method of all opaque constructions in use.
Calculation methods: EN-ISO / CIBSE / ASHRAE.
|
|
|
Opaque Total R-value
|
The total resistance of all layers of all opaque constructions in use (does not include inside and outside surface resistances).
|
|
|
Opaque Thermal mass Cm
|
The thermal capacity per unit area and temperature rise of all opaque constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Thermal mass class
|
The weight category describing the Thermal mass Cm of all opaque constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Is Ground contact floor?
|
Whether or not the construction is marked as a ground-contact floor.
|
|
|
Opaque Is Ground contact wall?
|
Whether or not the construction is marked as a ground-contact wall.
|
|
|
Opaque Is Green roof?
|
Whether or not the construction is marked as a green roof.
|
|
|
Opaque Thickness
|
The thickness of all opaque constructions in use calculated as the sum of the layer thicknesses.
|
|
|
Opaque Mass
|
The area density of all opaque constructions in use as calculated from the densities and thicknesses of the construction layers.
|
|
|
Opaque Outside Surface Emissivity
|
The emissivity of the outside surface of all opaque constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Inside Surface Emissivity
|
The emissivity of the outside surface of all opaque constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Outside Surface Resistance
|
The thermal resistance between the outside of a surface and its environment for all opaque constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Inside Surface Resistance
|
The thermal resistance between the inside of a surface and its environment for all opaque constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Outside Surface Solar Absorptance
|
The fraction of incident solar radiation absorbed by the outside of a surface for all opaque constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Inside Surface Solar Absorptance
|
The fraction of incident solar radiation absorbed by the inside of a surface for all opaque constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Outside Surface Visible Light Reflectance
|
The reflectance of visible light by the outside of a surface for all opaque constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Inside Surface Visible Light Reflectance
|
The reflectance of visible light by the inside of a surface for all opaque constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Regs Door type
|
The door type used for UK Building Regulations compliance testing for all door constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Regs Thermal Bridging Coefficient
|
The heat loss as a multiple of element area for non-repeating thermal bridging used for UK Building Regulations compliance.
|
|
|
Opaque Regs Data Source
|
The data source of all opaque constructions in use.
|
|
|
Opaque Regs Has Metal Cladding?
|
Opaque constructions can be identified as metal clad. This is used for thermal bridging in SBEM compliance testing.
|
|
|
Opaque Regs Is Curtain Wall?
|
Wall constructions can be identified as a curtain walls. This is used for UK Building Regulations compliance testing.
|
|
|
Opaque Regs Retain in Not/Ref Building?
|
If the construction belongs to the Partition or Floor/ceiling categories this additional parameter must be set for UK Building Regulations compliance testing.
|
|
|
Glazed Construction
|
The construction name and id of all glazed constructions in use.
|
|
|
Glazed U-value
|
The U-value as calculated by the user selected method of all glazed constructions in use.
Calculation methods: EN-ISO / CIBSE / ASHRAE.
|
|
|
Glazed Glass U-value
|
The Glass only U-value as calculated by the user selected method of all glazed constructions in use.
Calculation methods: EN-ISO / CIBSE / ASHRAE.
|
|
|
Glazed Frame U-value
|
The Frame only U-value as calculated by the user selected method of all glazed constructions in use.
Calculation methods: EN-ISO / CIBSE / ASHRAE.
|
|
|
Glazed Net R-value
|
The total thermal resistance as calculated by the user selected method of all glazed constructions in use.
Calculation methods: EN-ISO / CIBSE / ASHRAE.
|
|
|
Glazed Total R-value
|
The total resistance of all layers of all glazed constructions in use (does not include inside and outside surface resistances).
|
|
|
Glazed g-value
|
The solar transmittance value of all glazed constructions in use.
|
|
|
Glazed Shading Coefficient
|
The ratio of the instantaneous heat gain at normal incidence transmitted by a particular glass/blind combination to that transmitted by a reference glass.
|
|
|
Glazed Transmittance
|
The transmittance value of the window for solar radiation at normal incidence for all glazed constructions in use.
|
|
|
Glazed Shading Devices
|
The local, internal and external shading devices attached to all glazed constructions.
|
|
|
Glazed Is Electrochromic?
|
Whether or not the glazed construction contains an Electrochromic layer.
|
|
|
Glazed Electrochromic Profile
|
The modulating profile which determines when the electrochromic glazing is active.
|
|
|
Glazed Frame Percentage
|
The material percentage of the glazing element taken up by the frame.
|
|
|
Glazed Frame Absorptance
|
The ratio of the amount of radiation absorbed by a surface to the amount of radiation incident upon it.
|
|
|
Glazed Frame Resistance
|
The thermal resistance of the frame.
|
|
|
Glazed Frame Outside Surface Area Ratio
|
The outside surface area ratio of this frame. This is the material percentage of the outside surface taken up by the frame.
|
|
|
Glazed Frame Inside Surface Area Ratio
|
The inside surface area ratio of this frame. This is the material percentage of the inside surface taken up by the frame.
|
|
|
Glazed Frame Type
|
The type of frame material used in UK Part L compliance testing.
|
|
|
Glazed Outside Surface Emissivity
|
The emissivity of the outside surface of all glazed constructions in use.
|
|
|
Glazed Inside Surface Emissivity
|
The emissivity of the outside surface of all glazed constructions in use.
|
|
|
Glazed Outside Surface Resistance
|
The thermal resistance between the outside of a surface and its environment for all glazed constructions in use.
|
|
|
Glazed Inside Surface Resistance
|
The thermal resistance between the inside of a surface and its environment for all glazed constructions in use.
|
|
|
Glazed Regs Type
|
The window type.
|
|
|
Glazed Regs Surface Area Ratio
|
The “developed area to projected area” ratio for the window or rooflight.
|
|
|
Glazed Regs Thermal Bridging Coefficient
|
The heat loss as a multiple of element area for non-repeating thermal bridging used for UK Building Regulations compliance.
|
|
|
Glazed Regs Data Source
|
The data source of all glazed constructions in use.
|
|
|
Glazed Regs Is Display Window?
|
Whether or not the window is a display window.
|
|
|
Glazed Regs Use BFRC data values?
|
Whether or not the window uses values as defined under the conventions of the British Fenestration Rating Council.
|
|
|
Glazed Regs g-value
|
The solar transmittance value as defined by the BFRC.
|
|
|
Glazed Regs Light Transmittance
|
The light transmittance value as defined by the BFRC.
|
|
|
Glazed Regs Glazing Type
|
The glazing type used for dwellings under UK Building Regulations compliance testing.
|
|
|
Glazed Regs Sky Blocked
|
The degree of shading used for dwellings under UK Building Regulations compliance testing.
|
|
|
Room Group* 2015FP1
|
The room group the zone is assigned to, based on the grouping scheme.
|
|
|
Layer* 2015FP1
|
The layer the zone is assigned to.
|
|
|
Surface Adjacent Condition
|
The boundary condition used by Apache for thermal calculations.
|
|
|
Surface Area
|
The total surface area (not taking into account any adjacencies or openings).
|
|
|
Surface Tilt
|
The surface rotation angle, in degrees, from horizontal.
|
|
|
Surface Orientation
|
The surface rotation angle, in degrees, clockwise from north.
|
|
|
Surface Reflectance
|
The proportion of light striking the surface which will be reflected off of it.
|
|
|
Opening Area
|
The total opening area.
|
|
Infrared Standard
|
|
|
Infrared Cold
|
|
|
Infrared Warm
|
|
|
Infrared Hot
|
|
|
Spectrum Full
|
|
|
Spectrum Part
|
|
|
Spectrum Cold
|
|
|
Spectrum Mid
|
|
|
Spectrum Warm
|
|
|
Spectrum Hot
|
|
|
Mono Brown
|
|
|
Mono Sepia
|
|
|
Mono Blue
|
|
 |
 |
