What is the Apache View?
The Apache View is a view within the Virtual Environment’s Thermal category.
Apache is the name given to the thermal analysis programs in the Virtual Environment. The Apache view provides facilities for:
-
Preparation of input data for the thermal analysis programs; ApacheSim ASHRAE Loads and CIBSE Loads
-
Calculations and simulations using; ApacheSim, ApacheHVAC, MacroFlo, ASHRAE Loads and CIBSE Loads.
The preparation of thermal input data consists of three main tasks:
-
Specification of building location and weather data
-
Specification of building element data (properties of the building fabric)
-
Specification of space data (conditions in each space)
The interfaces to the thermal analysis programs provide facilities for:
-
Setting up the calculations and simulations
-
Specifying the results to be recorded
Context of ApacheView
To put the Apache view in context, it is useful to examine the steps involved in creating a thermal model and running the thermal analysis programs. This outline is intended as a guide. Many of the steps may be interchanged and data of all types may be edited at any stage.
Creation of building geometry
-
Start the Virtual Environment.
-
Enter the ModelBuilder Category and create the building geometry in ModelIT.
-
During this phase you may find it helpful to use Templates. Templates contain collections of data for thermal and other applications, and are created using the Template Manager. When a template is set as the
active template, its data is automatically assigned to spaces or elements as they are created.
Assignment of Apache thermal data
1. Select the Thermal Category.
2. Enter the Apache view.
3. Run the APlocate utility to define site location and weather data (for thermal and solar shading calculations).
4. Run the utility APcdb to define constructions.
5. Assign constructions to building elements as appropriate.
6. Run the utility APpro to define operational profiles.
7. Define the characteristics of the building’s HVAC systems using Apache Systems and assign systems to spaces.
8. For each space, assign Space Data to specify heating and cooling, internal gains and ventilation.
9. Use Space Thermal Templates to facilitate the previous two steps.
Assignment of other thermal and solar data
At this stage (or at any suitable time) you may wish to leave the Apache view to carry out the following additional tasks:
-
Within the MacroFlo View set up opening air flow characteristics for the MacroFlo simulation program.
-
Within the ApacheHVAC View set up HVAC system data for the ApacheHVAC simulation program.
-
Within the SunCast view of the Solar Category perform solar shading calculations.
Thermal analysis and results review
1. In the Apache view, perform either of the following analyses:
Overview of the ApacheView Interface Features
The Apache view consists of the following interface features:
Virtual Environment menu bar
These menus provide functions used throughout the Virtual environment and Apache view. Please refer to the
Virtual Environment User Guide for further information.
Apache edit toolbar
These icons provide a quick route to functions on the Apache menu bar.
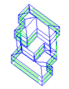
Model workspace
This displays the model geometry and provides a graphical means of selecting geometrical objects.
Model view toolbar
This provides functions for manipulating the view of the geometrical model.
Model Browser
This list of spaces, opening up to display surfaces and openings in those spaces, provides an alternative way to view and select geometrical objects.
Space Group tools
These tools allow the creation, application and selection of Space Grouping Schemes. See the ModelIT user guide for further information.
Thermal analysis buttons
These buttons invoke the thermal analysis programs CIBSE Loads, ASHRAE Loads and ApacheSim, and Batch Simulation.
When the Loads Methodology on the Apache View Settings menu is set to ASHRAE, CIBSE Loads is replaced by ASHRAE Loads.
Common tools for model viewing and interrogation
Before using the Apache view you should familiarise yourself with the following tools, which provide the means for navigating around the model to view and set space and building element attributes:
· The Virtual Environment menu bar
· The model workspace
· The model browser
· The model view toolbar
In particular, you should be familiar with the following procedures described in the ModelIT User Guide:
· Selecting a view of the model workspace using the following buttons on the model view toolbar:
o Fit view
o Zoom window
o Zoom in
o Zoom out
o Pan
o Zoom previous
o Zoom next
o View axis (Plan, Right, Left, Front, Back, Axon.)
o Set axonometric rotation
o Rotate view
· Selecting a single space or a set of spaces by clicking in the model workspace.
· Selecting a single space or a set of spaces by clicking in the model browser.
· Panning and zooming the model image.
· Moving between the following model decomposition levels using the up and down arrows on the view toolbar (or by double-clicking on a space or surface):
· Model or HVAC Zone level (HVAC Zone mode allows HVAC zones to be selected on the canvas and disables access to the lower levels of decomposition)
· Space level (only surface mode applies in the Apache view)
· Surface level (opening or adjacency mode)
· Moving between model decomposition levels by clicking in the model browser.